

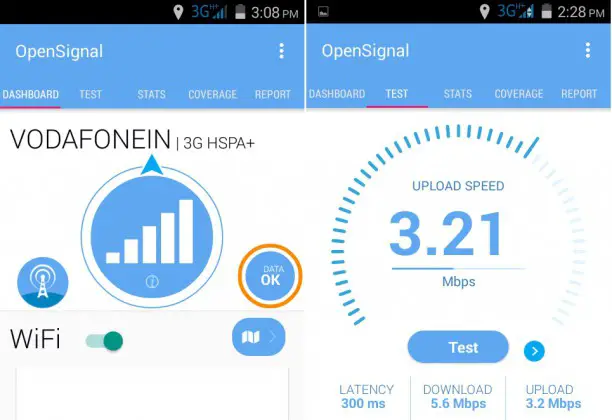
- Ethernet status speed different than speed test software#
- Ethernet status speed different than speed test plus#
- Ethernet status speed different than speed test download#
A satellite connection draws from a signal literally beaming down from space, which makes for much higher latency and vastly limits the amount of bandwidth you can get. Satellite internet is the slowest type of internet you can get. DSL maxes out at 140 Mbps, but many DSL users experience much slower speeds due to the technical limitations of a DSL connection.ĭSL’s copper wire connections deteriorate in strength as the user gets farther away from a central server, which makes for particularly slow connections in rural areas, suburbs, and the outskirts of cities. The internet connection draws entirely from 5G wireless networks, which makes it very fast but also slightly unstable-so your speeds can vary considerably throughout the day, and you may experience occasional disconnects.ĭSL internet is a somewhat outdated internet service that seems slower and slower as cable and fiber providers increasingly raise their speeds. A relatively new technology, 5G can be found mostly in urban areas through cellular providers Verizon and T-Mobile. But for most people, it’s as good as it gets for bandwidth.ĥG internet doesn’t have the same impressive bandwidth as fiber or cable, but it’s much faster than more antiquated internet types like DSL. Cable internet has much slower upload speeds compared to fiber, and it also can’t deliver impressive (albeit unnecessary) multigigabit speeds.
Ethernet status speed different than speed test download#
Symmetrical uploads mean you can get up to gigabit-speed throughput on uploads as well as downloads, vastly boosting your ability to hold video calls, upload large files to the internet, and post to social media.Ĭable internet is often just as fast as fiber internet, at least for download speeds. Nobody really needs internet that fast (not yet, at least), but fiber also speeds ahead of other internet types because it has symmetrical upload speeds. For more information, go to Comparing bandwidth for different internet typesįiber-optic internet gives you the most bandwidth and the fastest internet speeds, with internet plans topping out at a ridiculous 10,000 Mbps.

For 5GIG speed, single device wired speed maximum 4.7Gbps. Actual customer speeds may vary based on a number of factors and are not guaranteed. Internet speed claims represent maximum network service capability speeds and based on wired connection to gateway. ║Price after $5/mo Autopay & Paperless bill discount (w/in 2 bills).
Ethernet status speed different than speed test software#
Actual Internet speeds are not guaranteed and may vary based on factors such as hardware and software limitations, latency, packet loss, etc. Upload/download speed and device streaming claims are based on maximum wired speeds. If you live in an apartment or condo, Google Fiber’s ability to construct and provide Fiber is subject to the continued agreement between Google Fiber and the property owner.
Ethernet status speed different than speed test plus#
§Terms and Conditions: Plus taxes and fees. †Limited time offer subject to change valid to qualified residential customers who have not subscribed to any services within the previous 30 days and who have no outstanding obligation to Charter. *For the first 12 months with a 1-year agreement. Faster speeds and higher bandwidths mean you can support more devices and do a lot more things online. You can get faster speeds through a fiber connection with a 5 Gbps bandwidth than on a cable connection with a 1 Gbps bandwidth.
The bottom line is bandwidth can affect speed, but speed can’t go higher than bandwidth. Similar problems apply to an internet connection, reducing your speed. A clogged line can reduce the flow, or a faulty pipe-you name it. Of course, there are issues that can prevent you from filling that sink at the rate you expect. This example represents a fast connection. This example represents a slow connection.īut, if you open up each faucet to its maximum flow, the big faucet fills the sink faster than the medium-sized and small ones. A trickle takes forever and a day to fill that sink, right? The size of the faucet doesn’t matter, either-it’s a 10 Mbps flow, and that’s all you get. Now picture internet data as a flow of digital water. Underneath each faucet is a huge sink-this is your device, ready to download. There are big ones and medium-sized ones and small ones-we’ll pretend they represent fiber, cable, and DSL, respectively. The best way to explain the difference between speed and bandwidth is to use the faucet and sink analogy (although the car and highway one works too).įirst, picture your bandwidth as a faucet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
